
Like all hypothesis testing, the one sample t test determines if there is enough evidence reject the null hypothesis (H0) in favor of an alternative hypothesis (H1). Often, this designated value is a mean previously established in a population, a standard value of interest, or a mean concluded from other studies.
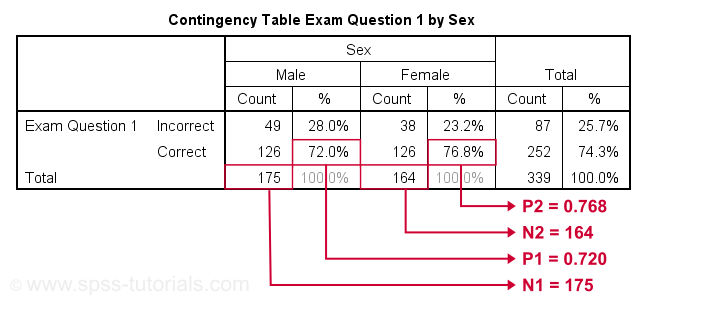
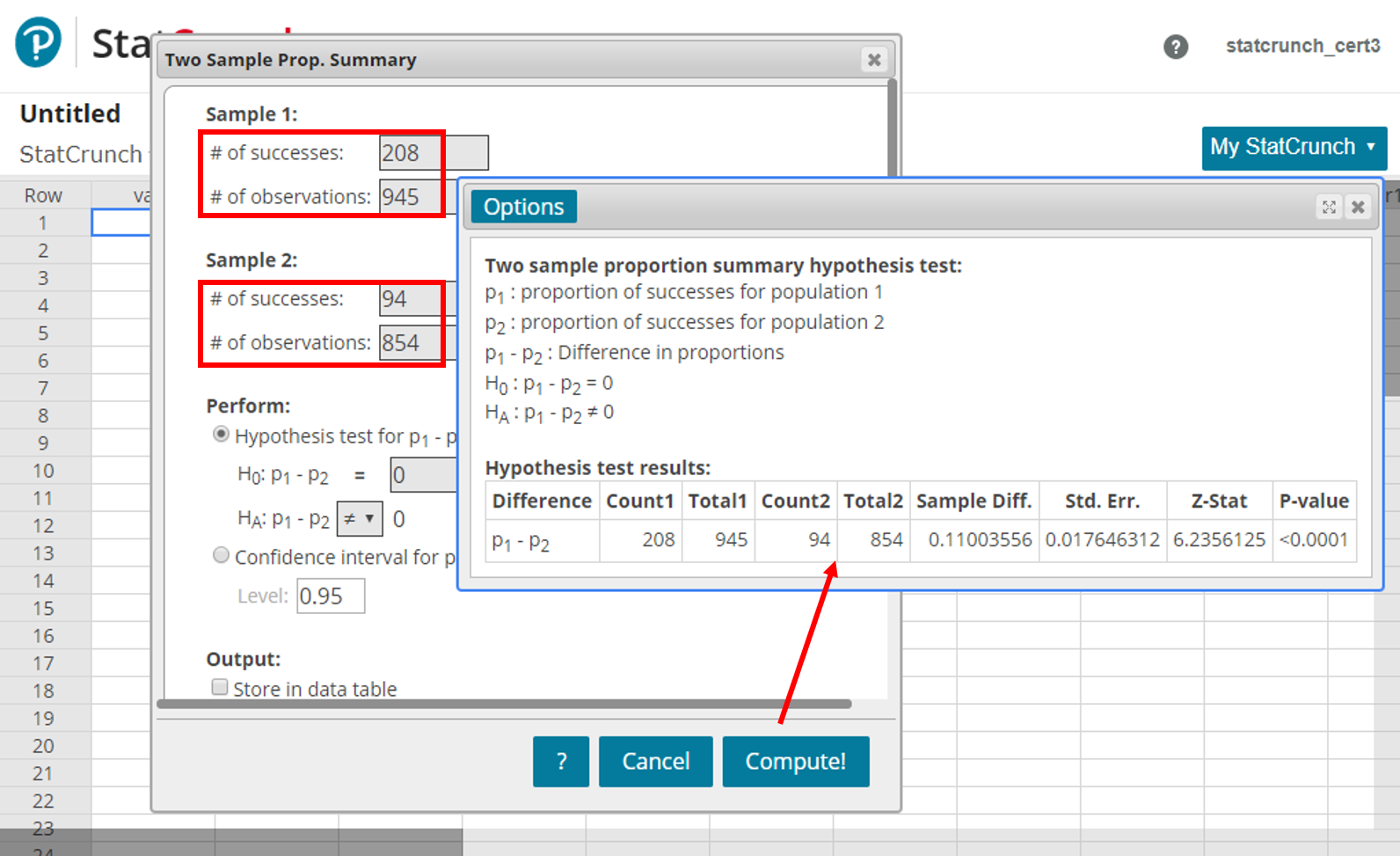
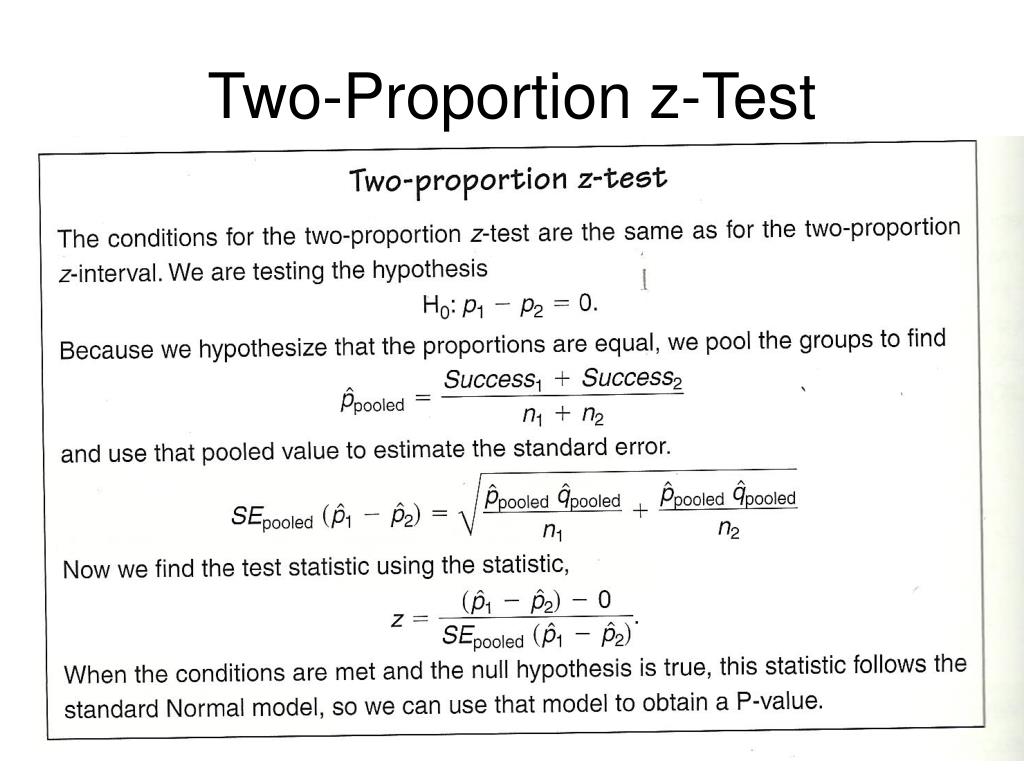
This designated value does not come from the data itself, but is an external value chosen for scientific reasons. The one sample t test, also referred to as a single sample t test, is a statistical hypothesis test used to determine whether the mean calculated from sample data collected from a single group is different from a designated value specified by the researcher. To do a hypothesis test at a 98% confidence level, add the argument this article you will learn the requirements and assumptions of a one sample t test, how to format and interpret the results of a one sample t test, and when to use different types of t tests. We can also say that the difference between the percentage of men and women who have Type 2 diabetes is 5.5% with a margin of error of 3.5%.ĭ & = \mbox (0.09021837 - 0.055) \\ At the 95% confidence level, we can say that the difference in proportion between diabetic men and diabetic women is between 0.02 and 0.09, higher for men than women. The hypothesis test shows that the difference is statistically significant with a P-value of 0.00201. # 2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
